"This is one of the most important questions that interviewer might be asking in an interview.Infyosis,Linked group,Kyndryl,Vodafone Idea, IBM and Mphasis etc."
INTRODUCTION:
It is said to be set operators which is used to combine, add or concatenate two or more result sets. It is used in the multiple select statements where to combine to produce the final desired results. In other words, multiple select statements of similar column name in same order and having same data type to produce the unified result. It merges the content of the two structurally compatible organized tables into single table.
In MIS datalake,when you are adding the modules of GST reconciliation which is to be used in micros in Excel or VB script, union and union all set operator is preferred for eliminating duplicate records or keeping duplicate records as per business requirement. There are several alternatives like bulk collect,join,set operators like intersect & minus for combining the data from the multiple tables.
Column must be of the same datatype for these operations of one select statement with another select statements. Columns must be in the same order in this set operators in the multiple select statements. Same number of columns should be used in the multiple selecting while using these operators. It can be defined as:" It is the type of set operators which is used in the database for obtaining the result set by combining multiple tables."
The output of the query contains the same column name and order which is the first select statement column name and order. Same columns and order will be the same in the multiple select statements. The numbers of column and order should be the same in the multiple select statements and each column having same data type.
One can say that the join and union are different thing. Join are combining the data from the different tables, but union is used to combine the data from the same table. Join append the table data horizontally or by adding more rows. whereas the union combines the table's data vertically or by adding more columns.
With the help of window function, elimination of the duplicate rows is possible. It is used to combine the result set of two or more select statements.
DIFFERENCE:
|
UNION
|
UNION ALL
|
|
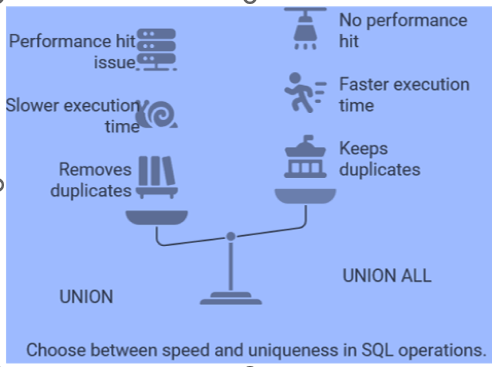
It keeps the
unique records of rows.
|
It keeps the
duplicate records of the rows.
|
|
Execution
time is more as it removes the duplicates.
|
Execution
time is less.
|
|
Select column_names
from table1 where conditions
Union
Select
column_names from table2 where
Conditions
|
Select
column_names from table1 where conditions
Union all
Select
column_names from table2 where
Conditions
|
|
Slow
performance is due to elimination of duplicate records.
|
Fast
performance is due to presence of duplicate records.
|
|
Performance
hit issue because load on database server to delete the duplicate rows.
|
Performance
hit issue is not observed.
|
|
It is slower
than union all.
|
It is faster
than union.
|
|
Result set is
sorted in ascending order. In other words, output is sorted by default.
|
Result set is
not sorted in ascending order. In other words, output is not sorted by default.
|
|
It is more
preferred by the database users.
|
It is less
preferred by the database users.
|
QUERY:
The below queries and screenshots are shared to practice the coding related to the topics.
The two table twitter and LinkedIn had been created for showing the output.
In the table twitter, name and location column names had been created with the datatype's varchar (20) & varchar (30). By using INSERT ALL statement, three rows had been inserted in the table twitter.
By using select * from twitter, we can find out the three records which had been inserted are displayed.
In the table LinkedIn, name and location column names had been created with the datatype's varchar (20) & varchar (30)
In the similar manner, by using INSERT ALL statement, three rows had been inserted in the table Linkedin. By using select * from Linkedin, we can find out the three records which had been inserted are displayed. With the help of update statement name 'Marry' had been changed into Liza.

Hence, the final result of the two tables i.e. twitter & LinkedIn in which all the rows present in the both tables are displayed in the screenshot.

Hence, the final result of the two tables i.e. twitter & LinkedIn in which the duplicate rows are present once in both tables are displayed in the screenshot. Only unique records are displayed.
Thus, comparison of both operators in terms of output to be displayed. In the left snapshot, there are no duplicate rows or records to be displayed. In the right snapshot, there are duplicate rows or records to be displayed. In the left snapshot, four rows are displayed whereas in the right snapshot, six rows are displayed.
select * from employee
In the table employee, four rows had been inserted which is displayed with the above query.
desc employee;
With the help of desc statement, the name of the column of the table employee i.e name and its relevant data type is varchar2(10)
create table department(name varchar(10));
Table department had been created with the single column name i.e. name with datatype varchar (10).
desc department;
Table department details created had been displayed.
insert into employee
select 'Rahul' from dual
union
select 'Rakesh' from dual
union
select 'Monkey' from dual
union
select 'Tiger' from dual
Four records or rows are to be inserted into the table employee.
insert into department
select 'Rahul' from dual
union
select 'Rakesh' from dual
union
select 'Monkey' from dual
union
select 'Tiger' from dual
Four records or rows are to be inserted into the table department.
It displays the output when both the tables employee and department, four records are inserted separately.
select * from employee
select * from department
By the above both queries, it will display all the records which are present in the employee and department table respectively.
select * from employee
union
select * from department
The result of the above query is shown with the help of screenshot.Eliminate duplicate records and keep the unique records from the both table employee & department.
select * from employee
union all
select * from department
The result of the above query which includes the duplicates of the rows .Rahul,Rakesh,Monkey and Tiger are repeated more than one times in the result.
select * from employee e join department d
on e.name=d.name
Join operation are performed on the both tables employee and department.Results of both the tables are represented in the horizontal manner.Name and Name_1 are the similar tables which contain the identical data.
select to_date(sysdate,'dd-mm-yyyy') from dual
union
select to_date(sysdate,'dd-mm-yyyy') from dual
select to_date(sysdate,'dd-mm-yyyy') from dual
union all
select to_date(sysdate,'dd-mm-yyyy') from dual
Interview may be asking you to write the query to display date in the form of DD-MM-YYY form.
Common Interview Questions asked on this topic:
Q1) Kindly confirm whether the order of rows is preserved in union and union all.
Ans No, neither union nor union all the order of rows is preserved. ORDER BY clause is used at the end of query for specified the order in ascending or descending order.
Q2) Does union and union all require the number and data types of columns to match?
Ans. Yes, both of them require the same number of columns in each select statement and corresponding columns must have the compatible data types.
Q3) When you should use union or union all?
Ans When to use Union:
- You want to eliminate the duplicate rows.
- You do not mind the lower performance.
- Data integrity is the concern where duplicate could cause issues.
When to use Union all:
- You want to include all the records using duplicates.
- You care about the performance and know that the duplicate will not cause any problems or issues.
Q4) Can we use union and union all inside the PLSQL cursor?
Ans Yes, we can use union and union all inside the PLSQL cursor.
Q5) How would you handle union operations in dynamic sql using PLSQL?
Ans EXECUTE IMMEDIATE is used for handling dynamic sql.
Q6) Write the query to combine the results from the different data types in the corresponding columns and how to ensure compatibility?
Ans For ensuring the compatibility, you can cast the columns to the data type.
select column1, CAST (column2 as varchar) AS column2 from table1
union
select column1, column2 from table2
Q7) What are the other set operators?
Ans. INTERSECT: It will return only rows which are present in both tables or result sets and removing duplicates.
INTERSECT ALL: It will return only rows which are present in both tables or result sets and including duplicates.
MINUS: It will return rows from the first result set or table which does not appear in the second result set or table & removing duplicates.
MINUS ALL: It will return rows from the first result set or table which does not appear in the second result set or table & including duplicates.



















Comments
Post a Comment